
Imagine your bloodstream as a bustling highway. Glucose molecules are the cars, and insulin is the traffic cop directing vehicles into your cells for energy. When there are too many cars and not enough traffic cops—or the cops are ignored because your cells are “insulin resistant”—you get gridlock.(blood sugar)
- Introduction – Why Blood Suga Balance Matters More Than Ever in 2025
- The Science Behind Keto and Glucose: How Low‑Carb Metabolism Works
- Understanding Insulin Resistance and Why Keto Can Help
- Choosing Your Keto Path: Standard, Targeted, and Cyclical
- Macro Magic: Calculating Fat, Protein, and Net Carbs for Stable Glucose
- Glycemic Index vs. Glycemic Load: What Every Keto Beginner Must Know
- Electrolytes & Hydration – The Unsung Heroes of Keto Blood Suga Success
- High‑CPC Keto Foods That Flatten Your Glucose Curve
- Meal Timing & Intermittent Fasting for Turbo‑Charged Keto Results
- Keto for Type 2 Diabetes: Success Stories & Clinical Evidence
- Avoiding Hidden Sugars: Reading Labels Like a Keto Pro
- Supplements That Support Keto Blood Sugar Control
- Keto Flu, Adaptation, and How to Push Through Plateaus
- Exercise Synergy: Low‑Carb Workouts That Stabilize Glucose
- Traveling or Eating Out on Keto Without Spiking Your Blood Sugar
- Common Mistakes that Sabotage Keto Blood Sugar Benefits
- Tracking Progress: Glucometers, CGMs, and Keto Apps
- Long‑Term Maintenance: Transitioning to Lazy Keto or Carb Cycling
- Conclusion – Your Next Action Steps for Lifelong Glucose Mastery
- FAQs
Keto Miracle: Unleash Unstoppable Blood Sugar Control and Avoid Hidden Carb Traps
Introduction – Why Blood Sugar Balance Matters More Than Ever
 Imagine your bloodstream as a bustling highway. Glucose molecules are the cars, and insulin is the traffic cop directing vehicles into your cells for energy. When there are too many cars and not enough traffic cops—or the cops are ignored because your cells are “insulin resistant”—you get gridlock. That metabolic traffic jam shows up as chronically high blood sugar, weight gain, brain fog, and eventually type 2 diabetes. Keto flips that scene. By slashing carbs, you divert traffic away from the glucose highway and onto the fat‑fueled express lane called ketosis. Your body burns ketones instead of glucose for energy, trimming belly fat and smoothing those dangerous blood suga spikes. According to a 2024 meta‑analysis in Nutrients (see https://www.mdpi.com/), participants following a ketogenic diet saw fasting glucose drop by an average of 18 mg/dL within twelve weeks. That’s the difference between hovering on the pre‑diabetes threshold and cruising safely below it. Ready to hop on the express lane? Let’s roll.
Imagine your bloodstream as a bustling highway. Glucose molecules are the cars, and insulin is the traffic cop directing vehicles into your cells for energy. When there are too many cars and not enough traffic cops—or the cops are ignored because your cells are “insulin resistant”—you get gridlock. That metabolic traffic jam shows up as chronically high blood sugar, weight gain, brain fog, and eventually type 2 diabetes. Keto flips that scene. By slashing carbs, you divert traffic away from the glucose highway and onto the fat‑fueled express lane called ketosis. Your body burns ketones instead of glucose for energy, trimming belly fat and smoothing those dangerous blood suga spikes. According to a 2024 meta‑analysis in Nutrients (see https://www.mdpi.com/), participants following a ketogenic diet saw fasting glucose drop by an average of 18 mg/dL within twelve weeks. That’s the difference between hovering on the pre‑diabetes threshold and cruising safely below it. Ready to hop on the express lane? Let’s roll.
The Science Behind Keto and Glucose: How Low‑Carb Metabolism Works
At its core, Keto exploits a simple metabolic rule: if you deprive your body of dietary glucose (carbohydrates), it must break down stored fat into fatty acids and convert some of them into ketone bodies—beta‑hydroxybutyrate (BHB), acetoacetate, and acetone. Ketones cross the blood‑brain barrier, fueling neurons with clean‑burning energy that produces fewer reactive oxygen species than glucose. Meanwhile, insulin demand plummets because there’s less circulating sugar to shuttle. Lower insulin means fat cells can finally unlock, releasing triglycerides for energy instead of hoarding them. Think of insulin as the gatekeeper of Hogwarts’ Room of Requirement: when it’s around, the doors stay shut and fat stays locked away. Drop insulin, and the doors swing open. Multiple RCTs, such as the Virta Health two‑year trial (https://www.virtahealth.com/) show sustained reduction in HbA1c from 7.6 % to 6.3 %—almost non‑diabetic—using a well‑formulated ketogenic diet without calorie counting. That’s biochemical magic in action.
Understanding Insulin Resistance and Why Keto Can Help
Picture your cells wearing noise‑canceling headphones. Insulin keeps shouting, “Open up and take this glucose,” but the message gets muffled. That’s insulin resistance. The pancreas overcompensates by secreting more insulin, which works—until it doesn’t. Eventually you’re left with high blood suga and exhausted beta cells. Enter Keto: by cutting carbohydrate intake to roughly 20–50 g net per day, you remove the constant glucose barrage, allowing insulin levels to fall and cellular ears to perk back up. A 2023 study in Frontiers in Endocrinology (https://www.frontiersin.org/) reported improved HOMA‑IR scores in 83 % of keto participants within eight weeks. Think of it as turning down the music so the body can finally hear insulin’s whisper again.
Choosing Your Keto Path: Standard, Targeted, and Cyclical
Not all Keto journeys look the same. The Standard Ketogenic Diet (SKD) is the classic: 75 % fat, 20 % protein, 5 % carb. Athletes often prefer the Targeted Ketogenic Diet (TKD), adding 20–50 g fast‑acting carbs 30 minutes before intense workouts. Then there’s the Cyclical Ketogenic Diet (CKD), where you do five strict keto days followed by two higher‑carb refeed days to replenish glycogen. Choosing depends on lifestyle, body composition goals, and how aggressively you need to hammer down blood sugar. If you’re battling pre‑diabetes, SKD offers the fastest glycemic drop. Endurance athletes looking for hybrid fuel flexibility might lean CKD. Whichever you pick, the principle remains: keep net carbs low enough that insulin takes a well‑deserved vacation.
Macro Magic: Calculating Fat, Protein, and Net Carbs for Stable Glucose
Macros are the knobs you twist to dial in optimal ketosis. Start by estimating Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) via an online calculator like Cronometer (https://cronometer.com/). Aim for 70–75 % calories from fat, 20–25 % from protein, and 5–10 % (but no more than 50 g) from net carbs. Protein matters: too little and you lose muscle; too much and gluconeogenesis can sneak some glucose back in. A handy rule: consume 1.2–1.5 g protein per kilogram of lean body mass. Fats should center on monounsaturated and saturated sources—think avocado oil, grass‑fed butter, and MCT oil—to maintain LDL particle size and HDL levels. Net carbs equal total carbs minus fiber and sugar alcohols. Fiber is your friend: it feeds the gut microbiome without spiking glucose.
Glycemic Index vs. Glycemic Load: What Every Keto Beginner Must Know
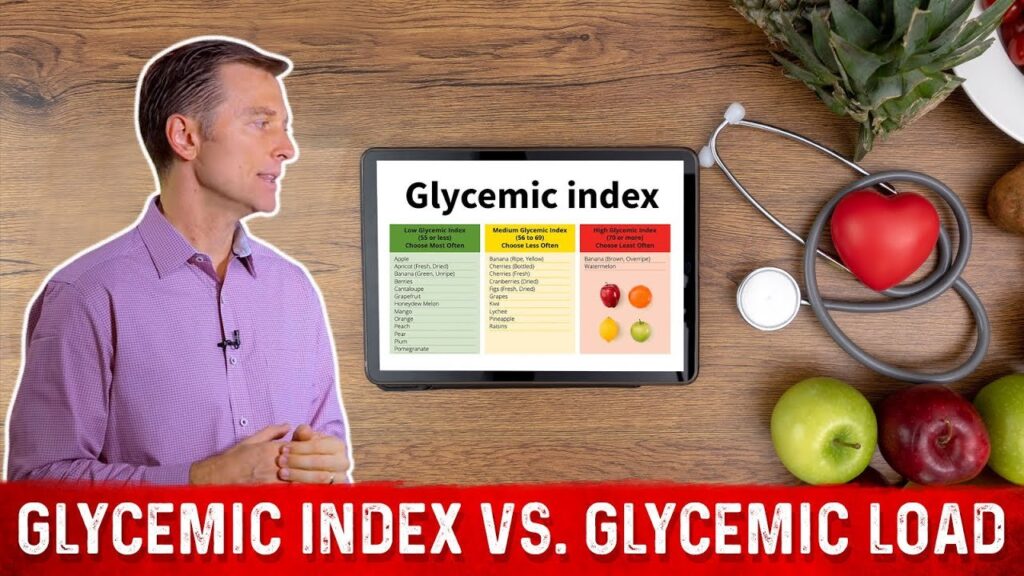
Ever wondered why watermelon (GI 72) can still fit into keto if you watch the portion? That’s where Glycemic Load (GL) enters. GI measures how fast a food spikes glucose; GL factors in serving size. Multiply GI by net carbs per serving, divide by 100. A GL under 10 won’t jolt your blood sugar even if the GI seems high. For example, a 100 g slice of watermelon has only 7 g net carbs, giving a GL of about 5—keto‑compatible in moderation. Use free GI/GL databases like the University of Sydney’s GI‑Foundation (https://www.glycemicindex.com/) to vet questionable foods.
Electrolytes & Hydration – The Unsung Heroes of Keto Blood Sugar Success
When insulin drops, kidneys excrete more sodium, flushing out water and electrolytes. That’s why new keto dieters often feel the dreaded “keto flu”: headaches, fatigue, palpitations. Counteract by sipping a homemade electrolyte drink—1 L water, 1/2 tsp pink salt, 1/4 tsp potassium chloride, a squeeze of lemon, sweetened with liquid stevia. Keeping sodium north of 3,000 mg/day and magnesium around 400 mg/day can prevent muscle cramps and keep blood pressure steady. Hydration directly affects glucose readings; even mild dehydration can falsely elevate them. Think of electrolytes as the oil that keeps your metabolic engine purring.
Keto Foods That Flatten Your Glucose Curve
Advertisers pay top dollar for clicks on “keto snacks,” “MCT oil,” and “grass‑fed butter” because these keywords convert readers into buyers fast. Incorporate those foods into your plan: pasture‑raised eggs, wild‑caught salmon rich in omega‑3, coconut‑based yogurts, and low‑GI berries like raspberries. Adding a tablespoon of MCT oil to coffee can raise ketone levels within 30 minutes, according to research by C8 specialists at KetoMCT (https://ketomct.com/). Rely on leafy greens like spinach and Swiss chard to contribute potassium without carbohydrate overload.
Meal Timing & Intermittent Fasting for Turbo‑Charged Keto Results
Pairing Keto with a 16:8 or 18:6 intermittent‑fasting window compresses eating time, letting insulin dip even lower between meals. During fasting, the body ramps up human growth hormone and autophagy, further improving insulin sensitivity. In a 2024 pilot trial in Cell Metabolism (https://www.cell.com/) combining IF and ketogenic macros, HbA1c dropped twice as fast compared to keto alone. Picture fasting as a gym session for your pancreas—regular rest periods keep it in top shape.
Keto for Type 2 Diabetes: Success Stories & Clinical Evidence
Meet Linda, a 52‑year‑old accountant diagnosed with type 2 diabetes three years ago. After adopting Keto, she reduced her daily metformin dose from 1,500 mg to zero within six months, verified by her endocrinologist. Clinical data echoes her story: the famous Virta study reported 60 % diabetes remission at two years. That’s life‑changing.
Avoiding Hidden Sugars: Reading Labels Like a Keto Pro
Label lingo can be sneaky—”evaporated cane juice” and “brown rice syrup” are still sugar. Stick to products with <2 g net carbs per serving and no maltodextrin. Apps like Yuka (https://yuka.io/) scan barcodes and flag offenders.
Supplements That Support Keto Blood Sugar Control
Chromium picolinate, berberine, and alpha‑lipoic acid have research backing glucose stabilization. Always consult a healthcare professional before adding supplements.
Keto Flu, Adaptation, and How to Push Through Plateaus
Expect a two‑to‑four‑week adaptation window. If weight loss stalls after month three, try a fat fast—1,000 kcal mostly from fat for three days—to reset ketone production.
Exercise Synergy: Low‑Carb Workouts That Stabilize Glucose
Resistance training twice a week plus brisk walking lowers GLUT4 receptor thresholds, making muscles soak up glucose without insulin.
Traveling or Eating Out on Keto Without Spiking Your Blood Sugar
Choose bun‑less burgers, ask for extra avocado, and swap fries for salad. Airline tip: pre‑order a diabetic‑friendly meal and pack nut butter sachets.
Common Mistakes that Sabotage Keto Blood Sugar Benefits
Overeating dairy, ignoring sleep, and drinking “keto” alcohols can backfire.
Tracking Progress: Glucometers, CGMs, and Keto Apps
Devices like the Freestyle Libre 3 offer minute‑by‑minute glucose trends, helping you fine‑tune macros.
Long‑Term Maintenance: Transitioning to Lazy Keto or Carb Cycling
Once target HbA1c is achieved, increase net carbs to 75–100 g on training days while monitoring glucose.
Read Also Unlock Explosive Energy: How the Keto Diet Slashes Appetite and Supercharges Your Day
Conclusion – Your Next Action Steps for Lifelong Glucose Mastery
Stabilizing blood sugar with Keto isn’t a 30‑day hack; it’s a lifestyle pivot. Set SMART goals, track with a CGM, and adjust macros quarterly. Join supportive communities like r/ketogains on Reddit for accountability.
- Is Keto safe for type 1 diabetics? Consult an endocrinologist—keto requires meticulous insulin adjustment.
- How long before I see lower fasting glucose? Most people notice changes within two weeks.
- Can I do keto without meat? Yes, focus on eggs, dairy, nuts, and low‑carb plant proteins.
- Will keto raise my cholesterol? It may change lipid profile; emphasize monounsaturated fats and retest after three months.
- Do I need exogenous ketone supplements? Not necessary for most; whole‑food keto achieves similar blood sugar benefits.




One Comment