Lower Blood Pressure Fast: Proven & Surprising Weight-Loss Strategies That Crush Hypertension Risk
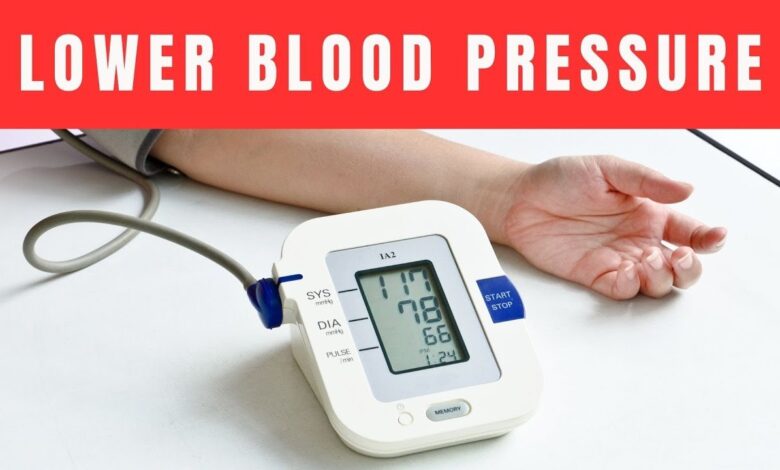
Lower blood pressure isn’t just a medical goal; it’s your passport to a longer, more vibrant life.
Outline
- Introduction – Why Weight Loss Is the Ultimate Lever to Lower Blood Pressure
- Understanding Blood Pressure Basics: What the Numbers Really Mean
- The Science Linking Excess Weight and Hypertension
- How Even Modest Weight Loss Lowers Blood Pressure Dramatically
- Real-World Study Highlights
- Setting a Safe and Realistic Weight-Loss Goal
- Nutrition First: Crafting a Heart-Smart, Weight-Loss Plate
- DASH Diet Demystified
- Low-Carb vs. Mediterranean: Which Wins?
- Calorie Deficit Without Deprivation: Practical Meal-Planning Hacks
- The Power of Protein for Satiety and Blood Pressure Control
- Micronutrients That Matter: Potassium, Magnesium, and More
- Move More, Pressure Less: Exercise Strategies That Burn Fat and Lower Blood Pressure
- Aerobic Workouts You’ll Actually Enjoy
- Strength Training for Metabolic Boost
- HIIT: A Time-Efficient Game Changer
- Beyond the Gym: Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT)
- Sleep, Stress, and the Cortisol-Hypertension Connection
- Smart Tech Tools: Wearables, Apps, and Digital Coaching
- Medication, Bariatric Surgery, and New Weight-Loss Drugs: When You Need More Help
- Building a Support System: Accountability Partners, Social Media, and Professionals
- Tracking Progress: Metrics That Matter for Blood Pressure and Weight
- Troubleshooting Plateaus Without Losing Momentum
- Sustainability Keys: Turning Short-Term Wins into Lifelong Habits
- Conclusion – Reclaim Your Heart Health by Lowering Blood Pressure Through Weight Loss
- FAQs
Introduction – Why Weight Loss Is the Ultimate Lever to Lower Blood Pressure
Lower blood pressure isn’t just a medical goal; it’s your passport to a longer, more vibrant life. Picture your arteries as a complex highway system—a slick network designed to move traffic (blood) smoothly from city to city (organ to organ). When you gain excess weight, it’s like dumping truckloads of debris onto every lane, forcing vehicles to squeeze through narrow gaps while revving their engines. Your heart, the eternal traffic cop, shouts “Move, move, move!” by pumping harder. That chronic overexertion raises blood pressure, damages arterial walls, and leaves you vulnerable to heart attack and stroke. Now imagine a road crew sweeping the lanes clean—that’s weight loss. Shedding as little as 5%–10% of body weight can ease arterial traffic, lower systolic and diastolic readings by 5–20 mm Hg, and slash cardiovascular risk by up to 30%. Those numbers aren’t hype; they’re highlighted in the American Heart Association’s “Managing Weight to Control High Blood Pressure” guidelines (heart.org). If you’ve ever wondered whether slimming down really matters—spoiler alert—it does, and dramatically. In fact, weight loss rivals top-shelf antihypertensive drugs for effectiveness, minus the pharmacy bill and potential side-effects. Ready to fire up your internal cleanup crew? Grab a water bottle, silence your inner skeptic, and dive into these proven strategies that not only torch fat but also lower blood pressure fast.
Read Also Can Weight Loss Lower High Blood Pressure? A Must Read.
Understanding Blood Pressure Basics: What the Numbers Really Mean
Before you charge into calorie-cutting, you need to decode the numbers your nurse rattles off during a check-up. Systolic pressure (the top number) measures the force when your heart contracts; diastolic (the bottom) gauges the pressure when the heart rests. Think of systolic as the “push” and diastolic as the “pause.” The gold-standard reading—120/80 mm Hg—means your cardiovascular plumbing is smooth, flexible, and leak-free. Hypertension begins at 130/80, a silent uptick that WHO calls “the global killer hiding in plain sight” (who.int). Each 20-point systolic or 10-point diastolic jump doubles your risk of deadly heart disease. Weight gain accelerates that climb because extra fat triggers hormonal havoc: insulin resistance, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system (RAAS) activation, and sympathetic nervous system overdrive—all of which constrict blood vessels like a vice grip. Translate: Higher numbers on the bathroom scale usually mean higher numbers on the blood-pressure cuff. By the end of this guide, you’ll not only know how to lower blood pressure but also how to keep it in the sweet spot for life.
The Science Linking Excess Weight and Hypertension
Why does carrying extra fat crank up your pressure gauges? Envision fat tissue as an overzealous warehouse manager stockpiling inflammatory chemicals—cytokines, leptin, and angiotensinogen. These messengers send frantic emails throughout your body, ordering blood vessels to tighten and kidneys to cling to sodium. Meanwhile, the heart is stuck on an exhausting double shift, pumping harder to move blood around a larger body mass. In clinical trials reviewed in the journal Hypertension (ahajournals.org), every kilogram of weight lost translated to a 1 mm Hg drop in systolic pressure. That’s not trivial. Lose 10 kg (22 lb), and you could drop your systolic reading by a full 10 points—often enough to graduate from Stage 2 hypertension to prehypertension without swallowing a single pill. The bottom line? Lose fat, gain freedom from the cuff.
How Even Modest Weight Loss Lowers Blood Pressure Dramatically
Let’s bust the myth that you need a magazine-cover six-pack to lower blood pressure. In one American Heart Association cohort study of 133,000 adults, a mere 5% weight reduction slashed hypertension incidence by 22% (www.heart.org). Why such outsized returns? First, fat cells shrink, dialing down inflammatory cytokines. Second, insulin sensitivity rebounds, trimming blood sugar spikes that stiffen arteries. Third, kidney filtration improves, letting you excrete sodium more efficiently—bye-bye water retention. Real-world example: Maria, a 52-year-old accountant, swapped soda for sparkling water, added 30-minute brisk walks, and lost 12 lb in three months. Her blood pressure plummeted from 145/92 to 126/82, shocking her doctor into reducing her medications. Maria’s story isn’t rare; it’s physiology 101.
Real-World Study Highlights
In 2024, Canadian researchers tracked obese volunteers using a new GLP-1 weight-loss drug and observed average nightly blood-pressure drops of 7/4 mm Hg (American Heart Association). That’s equivalent to many first-line antihypertensive prescriptions. Translation: Whether you melt fat through behavior, medication, or both, the cardiovascular payoff is enormous.
Setting a Safe and Realistic Weight-Loss Goal
Goals are the GPS of your health journey—skip them, and you’ll wander in circles. Aiming to “lose weight” is as vague as “drive somewhere nice.” Instead, lock in SMART targets: Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time-bound. For example, “Drop 15 lb in 12 weeks by cutting 400 calories a day and walking 8,000 steps” creates an actionable map. Most clinicians endorse losing 1–2 lb per week to preserve muscle and keep metabolism humming. Anything faster risks muscle loss and rebound weight gain. Calculate your daily calorie needs using the National Institutes of Health Body Weight Planner (free online tool) and subtract 500 calories for a sustainable deficit. Weight-loss pace matters—fast lanes can backfire like speeding tickets on your arterial highway.
Nutrition First: Crafting a Heart-Smart, Weight-Loss Plate
Food is chemistry, not morality, yet marketing often muddies the waters with villain-and-hero labels. Reframe your plate through three questions: “Does it nourish, does it satisfy, does it support lower blood pressure?” The sweet spot is a hybrid of the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) template—famous for its sodium-slashing, produce-packing ethos—and an energy-controlled Mediterranean approach rich in olive oil, legumes, and fatty fish. Aim for half your plate piled with colorful veggies, a quarter with lean protein, and the final quarter with whole grains or fibrous carbs. Sprinkle avocado or nuts for healthy fats that quell hunger hormones. Season with herbs instead of salt—your taste buds adapt in weeks.
DASH Diet Demystified
DASH isn’t a crash diet; it’s a sustainable blueprint backed by decades of NIH data. By capping sodium at 1,500 mg daily and prioritizing potassium-rich produce, DASH can lower systolic pressure by 8–14 mm Hg independent of weight loss. Combine it with a calorie deficit, and you’ve got a one-two punch to hypertension. Check the official NIH resource here: nhlbi.nih.gov.
Low-Carb vs. Mediterranean: Which Wins?
Low-carb enthusiasts tout rapid water-weight loss and better glycemic control, while Mediterranean fans emphasize long-term heart benefits. Meta-analyses show both diets can lower blood pressure, but Mediterranean patterns edge ahead on LDL cholesterol reduction. If carbs spike your cravings, a moderate low-carb plan (<130 g/day) can amplify weight loss without compromising nutrient intake. Ultimately, the best diet is the one you’ll follow—consistency trumps perfection.
Calorie Deficit Without Deprivation: Practical Meal-Planning Hacks
Nobody sticks to white-knuckle restriction forever; deprivation is the highway to binge city. Instead, fill up on low-energy-density foods—think broth-based soups, leafy salads, and fresh fruit—so your stomach feels satisfied while calories stay in check. Batch-cook lean proteins on Sundays, portion brown-rice cups, and pre-chop veggies to reduce weekday friction. Use free apps like MyFitnessPal or Cronometer to track intake and monitor sodium. Fancy a treat? Apply the 90/10 rule—eat nutrient-dense 90% of the time, reserve 10% for planned indulgences. Ignoring cravings is like holding your breath; you’ll eventually gasp.
The Power of Protein for Satiety and Blood Pressure Control
Protein isn’t just for bodybuilders—it’s a dieter’s secret weapon because it blunts ghrelin (“I’m hungry”) and boosts peptide YY (“I’m full”). Aim for 1.2–1.6 g per kilogram of ideal body weight daily. Lean chicken, fish, beans, and Greek yogurt supply amino acids without saturated-fat baggage. Higher protein intake also protects muscle during weight loss, keeping resting metabolic rate stable. Bonus: Certain protein sources (salmon, sardines) deliver omega-3s that further lower blood pressure by enhancing endothelial function.
Micronutrients That Matter: Potassium, Magnesium, and More
If macronutrients are the players, micronutrients are the coaches orchestrating victory. Potassium counters sodium’s pressure-raising effects by flushing excess fluid; aim for 3,500 mg daily via bananas, sweet potatoes, and spinach. Magnesium relaxes blood vessel walls—load up on almonds, black beans, and oats. Calcium regulates vascular contractions; low-fat dairy and fortified plant milks help you hit 1,000 mg. A daily multivitamin can fill small gaps, but food synergy beats pill isolates.
Move More, Pressure Less: Exercise Strategies That Burn Fat and Lower Blood Pressure
Physical activity is the turbocharger of weight loss and vascular health. The CDC prescribes at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly (cdc.gov), yet only 53% of adults meet that bar. Don’t fear: you don’t need a gym membership—brisk walking, cycling, or dancing at home counts. Exercise improves endothelial nitric-oxide production, relaxing arteries, and decreases resting sympathetic tone.
Aerobic Workouts You’ll Actually Enjoy
Enjoyment breeds adherence. Experiment with Zumba, pool jogging, or nature hikes until you find a “joy workout.” Shoot for 30-minute sessions, five days a week; break them into three 10-minute micro-bursts if your schedule’s jammed.
Strength Training for Metabolic Boost
Muscle mass is your metabolic furnace—each pound burns an extra 6–10 calories daily at rest. Two or three full-body sessions per week enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce visceral fat linked to hypertension.
HIIT: A Time-Efficient Game Changer
High-Intensity Interval Training alternates 30-second sprints with 90-second recoveries. In just 20 minutes, HIIT can torch calories and lower blood pressure as effectively as longer moderate sessions. Apps like Nike Training Club guide you through free routines.
Beyond the Gym: Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT)
NEAT is the unsung hero of caloric burn—fidgeting, lawn-mowing, walking the dog. Incremental tweaks (parking farther away, pacing during phone calls) can add 300–500 calories of daily expenditure without sweat-drenched workouts. Over a year, that could mean 30 lb of fat gone, easing arterial pressure naturally. Wear a step tracker and aim for 8,000–10,000 steps.
Sleep, Stress, and the Cortisol-Hypertension Connection
Skimping on sleep or marinating in stress bathes your body in cortisol—the hormone that cues your liver to release glucose and your vessels to constrict. Chronic cortisol spikes sabotage weight loss and ratchet up blood pressure. Prioritize 7–9 hours of quality sleep: dark room, cool temp, and tech-free 60 minutes before bedtime. Combat stress with mindfulness apps like Headspace, deep-breathing drills, or yoga flows. Remember, relaxation isn’t a luxury; it’s hypertension therapy.
Smart Tech Tools: Wearables, Apps, and Digital Coaching(Lower Blood Pressure)
Technology turns your smartphone into a mini cardiology lab. Devices like Withings BPM Connect log readings directly into Apple Health. Pair that with a calorie-tracking app and a smartwatch measuring heart-rate variability, and you’ve created a closed feedback loop. Some insurers offer premium discounts when you share activity data—saving money while you save arteries.
Medication, Bariatric Surgery, and New Weight-Loss Drugs: When You Need More Help
Lifestyle is king, but genetics and comorbidities sometimes call for reinforcements. GLP-1 agonists (semaglutide, tirzepatide) deliver double-digit weight loss and measurable blood-pressure drops. Talk to a clinician about eligibility and cost (some coupons offset steep price tags). For BMIs above 40—or above 35 with complications—bariatric procedures like sleeve gastrectomy can cut systolic pressure by 30 points and diabetes remission by 60%. Always weigh surgical benefits against potential risks with a board-certified surgeon.(Lower Blood Pressure)
Building a Support System: Accountability Partners, Social Media, and Professionals
Humans are wired for community. A 2023 study showed dieters with a weekly accountability buddy call lost 35% more weight than solo strivers. Whether it’s a buddy, a Facebook group like “LoseIt—Healthy Weight Loss Support,” or a registered dietitian, outside eyes keep you honest and motivated. If budget allows, hire a certified personal trainer or health coach; the investment often pays itself back in medical-bill savings.
Tracking Progress: Metrics That Matter for Blood Pressure and Weight
Scale weight is only one data point. Track waist circumference (goal <40 in for men, <35 in for women), body-fat percentage, resting heart rate, and of course weekly blood-pressure averages. Use spreadsheets or apps like Lose It! to visualize trends. Celebrate non-scale victories—fitting into old jeans, climbing stairs without panting—because success is multifaceted.
Troubleshooting Plateaus Without Losing Momentum
Weight-loss stalls are biology’s way of testing your resolve. When the scale freezes for three weeks, re-audit calories (creep happens), tweak workouts (add HIIT), and prioritize protein. Consider a brief maintenance phase to reset hunger hormones. Plateaus aren’t failure; they’re practice laps for life after dieting.
Sustainability Keys: Turning Short-Term Wins into Lifelong Habits
Transformation is a marathon without a finish line. Ditch “diet” thinking; build rituals. Meal-prep Sundays, Wednesday weigh-ins, Friday dance workouts—anchor behaviors so ingrained they survive schedule storms. Remember, you’re not just losing weight; you’re engineering an environment where healthy choices are the default.
Read Also How Does the Keto Diet Help Control Blood Sugar?
Conclusion – Reclaim Your Heart Health by Lowering Blood Pressure Through Weight Loss
Lower blood pressure is the priceless dividend paid out when you invest in weight loss. From the first salad swap to the final mile jogged, every healthy choice widens your arterial highways, lowers that relentless cuff reading, and gifts you years of energy to spend on people and passions you love. Whether you’re starting with 5 lb or 50 lb to lose, today’s small step is tomorrow’s giant health payoff. Your heart is counting on you—literally.(Lower Blood Pressure)
FAQs
1. How quickly can weight loss lower blood pressure?
Most people see measurable drops within four weeks of consistent calorie deficit and exercise, though individual responses vary.
2. Do I need to reach my “ideal” weight to normalize blood pressure?
No. Losing just 5%–10% of your starting weight often lowers readings significantly.
3. Can I lower blood pressure through diet alone without exercise?
Yes, diet alone helps, especially DASH-style eating, but combining nutrition with physical activity offers the biggest benefit.
4. Are weight-loss medications safe for blood-pressure patients?
Many modern GLP-1 drugs are not only safe but also lower blood pressure; consult your doctor about side-effects and contraindications.
5. How often should I check my blood pressure during weight loss?
Home-monitor two to three times a week, log readings, and share trends with your healthcare provider at each visit for tailored guidance.





One Comment