
-
How does the keto diet really impact metabolism? If you’ve heard that the keto diet can boost your metabolism, you’re not alone. so,
How Does the Keto Diet Improve Your Metabolism?
Introduction
- Brief overview of metabolism and its importance in weight loss and overall health
- The keto diet’s primary goal and its impact on metabolism
- The growing popularity of the keto diet and its metabolism-boosting effects
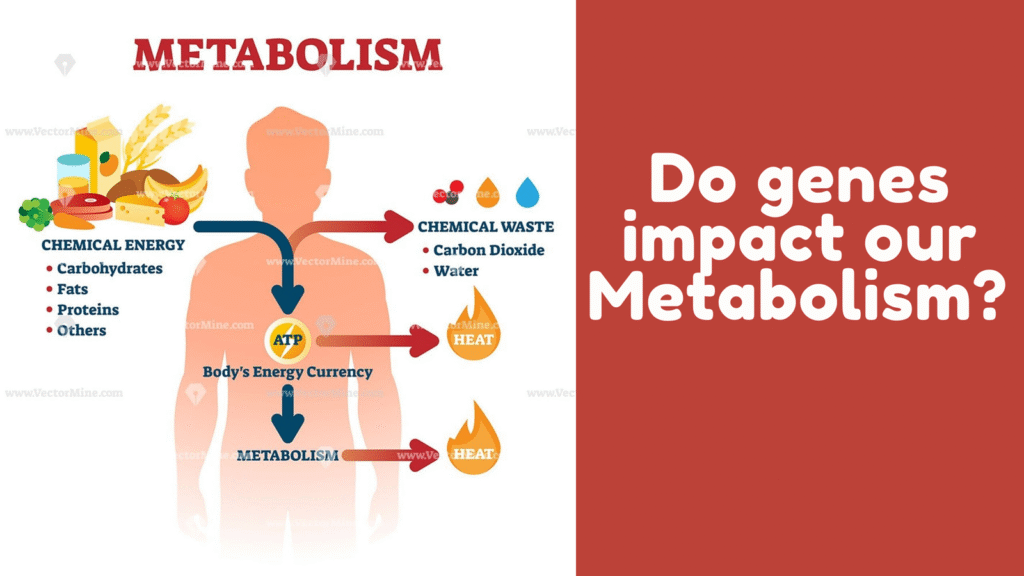
Understanding Metabolism
- What is metabolism?
- The two main components of metabolism: catabolism and anabolism
- How metabolism affects energy production, weight loss, and fat burning
The Basics of the Keto Diet
- What is the ketogenic diet?
- The macronutrient breakdown: High fats, moderate protein, and very low carbs
- How ketosis works and its effects on metabolism
How the Keto Diet Impacts Metabolism
- Transitioning from glucose to fat as the primary energy source
- How ketosis increases fat burning
- The role of ketones in energy production and metabolic efficiency
- How keto supports metabolic processes by improving insulin sensitivity
Fat Burning and the Keto Diet
- The science behind fat burning on keto
- How ketosis encourages the body to burn stored fat for energy
- How the body’s fat-burning mechanisms work while on keto
How the Keto Diet Enhances Insulin Sensitivity
- Understanding insulin resistance and its role in metabolism
- How the keto diet reduces insulin spikes and improves insulin sensitivity
- The long-term benefits of better insulin management on metabolism and fat loss
Increased Energy Expenditure with the Keto Diet
- The role of the thermic effect of food (TEF) on metabolism
- How the keto diet’s high-fat content impacts TEF and increases energy expenditure
- Why the keto diet may make the body burn more calories at rest
The Impact of the Keto Diet on Hormones
- How the keto diet affects key metabolic hormones like ghrelin, leptin, and cortisol
- The relationship between insulin, leptin, and fat storage
- Why the keto diet may help control hunger and reduce food cravings
The Role of Muscle Mass and Protein Synthesis
- How the keto diet helps preserve muscle mass during weight loss
- The importance of protein in metabolic function
- How maintaining muscle mass boosts metabolism
Keto Diet and Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR)
- What is Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR)?
- How the keto diet influences RMR and calorie burn at rest
- Studies supporting keto’s role in maintaining or increasing RMR
The Thermogenic Effect of Ketosis
- How ketosis increases the body’s heat production (thermogenesis)
- The benefits of thermogenesis in boosting metabolism and fat burning
- Why the keto diet may lead to higher calorie expenditure throughout the day
Long-Term Effects of the Keto Diet on Metabolism
- How prolonged adherence to the keto diet impacts metabolism
- Metabolic adaptation and why some people experience faster weight loss than others on keto
- The importance of re-feeding days or cycling on keto for long-term metabolic health
Risks and Considerations of the Keto Diet
- Potential downsides of the keto diet on metabolism
- The “keto flu” and its temporary metabolic effects
- When and why you might need to cycle off keto for metabolic health
- How to Maximize Metabolic Benefits on the Keto Diet
- Incorporating exercise for improved metabolism while on keto
- Hydration and electrolytes for optimal metabolic function
- Key tips for sticking to keto and enhancing metabolism
Conclusion
- Recap of how the keto diet boosts metabolism
- Final thoughts on the importance of combining diet and lifestyle for effective metabolic health
FAQs
- How long does it take for the keto diet to improve metabolism?
- Can the keto diet be sustainable for long-term metabolic health?
- Does the keto diet work for everyone when it comes to improving metabolism?
- Can the keto diet help with other metabolic conditions besides weight loss?
- What are the key metabolic benefits of ketosis aside from fat loss?
How Does the Keto Diet Improve Your Metabolism?
In the world of weight loss and health optimization, the ketogenic (keto) diet has become a game-changer. But beyond its fame for fat loss, many people wonder: How does the keto diet really impact metabolism? If you’ve heard that the keto diet can boost your metabolism, you’re not alone. Thousands of people who have embraced keto claim it has not only helped them shed pounds but also increased their overall energy and metabolism. In this blog, we’ll explore the science behind how the keto diet improves metabolism and why it’s so effective at helping you lose weight and improve your health.
Introduction
Metabolism plays a vital role in our overall health, determining how our bodies convert food into energy. A faster metabolism generally helps with fat burning, energy expenditure, and even weight management. The ketogenic diet, known for its low-carb, high-fat approach, has been linked to significant improvements in metabolism, particularly in how your body burns fat.
But how does the keto diet improve your metabolism? Well, it’s all about shifting your body’s primary fuel source from carbohydrates (sugar) to fat. In the process, your body enters a state of ketosis, where it burns fat for energy instead of glucose. This shift not only helps you burn more fat but also improves your overall metabolic processes, making it easier to lose weight and maintain a healthy weight over the long term.
Understanding Metabolism
What is Metabolism?
Metabolism refers to the chemical processes by which your body converts food into energy. These processes include breaking down nutrients from food, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, and using them for energy or storing them for later use. There are two main components of metabolism: catabolism (breaking down molecules to release energy) and anabolism (building molecules to store energy).
The Two Main Components of Metabolism: Catabolism and Anabolism
Catabolism is the breakdown of food into smaller components to release energy. When we eat, our bodies break down carbohydrates into glucose (sugar), proteins into amino acids, and fats into fatty acids. These molecules then enter our bloodstream and are used by the body for energy.
On the other hand, anabolism is the process of building and storing energy. When you consume more calories than your body needs, the extra energy is stored in the form of glycogen (in muscles and the liver) or fat. However, if you have a slow metabolism, your body may store excess fat more easily than burning it.
How Metabolism Affects Energy Production, Weight Loss, and Fat Burning
Your metabolism directly impacts how efficiently your body converts food into energy. A faster metabolism means your body is burning energy more efficiently, which can lead to weight loss and increased fat burning. Conversely, a slow metabolism can result in weight gain and difficulty losing fat. A high metabolic rate is associated with better energy levels, improved fat burning, and a leaner physique.
The Basics of the Keto Diet
What is the Ketogenic Diet?
The ketogenic diet, commonly known as keto, is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate eating plan designed to put your body into a state of ketosis. Normally, your body burns glucose (from carbs) for energy, but when you drastically reduce carbs and increase fats, your body begins to burn fat for fuel instead.
The Macronutrient Breakdown: High Fats, Moderate Protein, Very Low Carbs
In the keto diet, approximately 70% of your calories come from healthy fats, 25% from protein, and only 5% from carbohydrates. This high-fat, low-carb approach forces your body to enter ketosis, where it begins to burn fat for fuel instead of carbs.
How Ketosis Works and Its Effects on Metabolism
When you reduce carbs to such a low level, your body runs out of glucose and starts breaking down stored fat into ketones, which become the primary energy source for your brain and body. This metabolic shift increases fat burning, reduces hunger, and stabilizes blood sugar levels, all of which help boost metabolism and support weight loss.
How the Keto Diet Impacts Metabolism
The keto diet, with its high-fat, low-carb approach, has garnered significant attention in the realm of weight loss and metabolic health. While it is well-known for promoting fat loss, the keto diet also significantly impacts metabolism in several ways. In this section, we’ll dive deeper into how the keto diet works with your metabolism and the remarkable effects it can have on energy production, fat burning, and overall metabolic efficiency.
Transitioning from Glucose to Fat as the Primary Energy Source
When you typically consume carbohydrates, your body breaks them down into glucose (sugar), which serves as its primary source of energy. This glucose is used by your cells for energy, and any excess is stored as fat for future use. However, on a keto diet, carbohydrates are drastically reduced, forcing your body to find an alternative fuel source.
By reducing carb intake to the point where your body’s glycogen stores are depleted, the liver begins to break down fat into molecules called ketones. These ketones become the body’s new energy source, replacing glucose. The transition from glucose to fat as the primary energy source is one of the key mechanisms that fuel the metabolism on the keto diet.
In this process, your body burns more fat, both from the food you eat and from your fat stores. This shift enhances fat burning, as the body becomes more efficient at converting fat into energy. Instead of storing fat, the body now uses it as its main energy source.
How Ketosis Increases Fat Burning
Ketosis is the metabolic state that occurs when your body shifts from burning glucose to burning fat for energy. This transition results in more efficient fat burning, as your body now has a constant, reliable supply of fat to convert into energy. When in ketosis, the body breaks down stored fat, leading to fat loss.
Ketones are not only a source of energy for the body but also play a significant role in enhancing metabolic efficiency. Ketones are a more energy-dense fuel than glucose, and they provide more long-lasting energy, especially for the brain. As a result, the body’s ability to burn fat improves while in ketosis, leading to a higher rate of fat loss compared to diets that primarily rely on carbohydrates.
Additionally, the process of fat breakdown into ketones and their subsequent use for energy increases overall metabolic activity. This means your body can burn fat for energy even while at rest, helping you achieve fat loss without needing to exercise for long periods of time.
The Role of Ketones in Energy Production and Metabolic Efficiency
Ketones are byproducts of fat metabolism, created when the liver breaks down fat into fatty acids. These ketones then enter the bloodstream and become the body’s primary energy source in a state of ketosis. One of the reasons the keto diet works so effectively for weight loss and metabolic health is that ketones are a more efficient energy source than glucose.
Unlike glucose, which requires a quick and constant supply of carbs to maintain energy levels, ketones provide a steady, long-lasting source of energy. The use of ketones helps to keep the metabolic processes running smoothly, even when carbohydrate intake is low. It also means that your body doesn’t experience the crashes or energy dips that can happen with carb-based energy systems.
Moreover, ketones produce less oxidative stress than glucose, meaning they are less likely to cause damage to cells and tissues. This reduction in oxidative stress can contribute to a more efficient metabolism over time and may protect against some of the chronic diseases associated with inflammation, such as diabetes and heart disease.
How Keto Supports Metabolic Processes by Improving Insulin Sensitivity
One of the most significant impacts the keto diet has on metabolism is its ability to improve insulin sensitivity. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels by allowing cells to take in glucose. When you consume carbs, your body releases insulin to manage the sugar spikes in your bloodstream.
However, over time, the constant consumption of high-carb foods can lead to insulin resistance, where your cells become less responsive to insulin, and your pancreas has to produce more of it. This condition is linked to a variety of metabolic issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
The keto diet reduces carb intake, which leads to lower insulin levels and more stable blood sugar levels. By maintaining low levels of insulin, the keto diet helps to improve insulin sensitivity. This is crucial for optimizing metabolism because insulin sensitivity allows your body to efficiently utilize glucose and fat for energy, rather than storing excess energy as fat.
As a result, the body becomes more adept at burning fat, leading to fat loss and improved metabolic function. By improving insulin sensitivity, the keto diet helps regulate blood sugar, prevent weight gain, and reduce the risk of metabolic diseases.
Increased Energy Expenditure with the Keto Diet
The thermic effect of food (TEF) refers to the energy required for the digestion, absorption, and metabolism of food. When you consume food, your body burns calories just to process the nutrients, and different macronutrients have different thermic effects. Proteins, for example, require more energy to digest than carbohydrates and fats.
Since the keto diet is high in fats and moderate in protein, it can increase the thermic effect of food. The body requires more energy to process fat compared to carbohydrates, which results in a higher rate of energy expenditure after meals. This increase in energy expenditure may contribute to weight loss, as more calories are burned during digestion and absorption.
Additionally, because the body relies on fat as its primary fuel source while in ketosis, it continually burns fat for energy throughout the day. This process increases energy expenditure even when you’re not actively exercising, leading to more efficient fat burning.
The Impact of the Keto Diet on Hormones
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, and the keto diet influences several key hormones that impact your metabolic processes. Here’s how:
How the Keto Diet Affects Key Metabolic Hormones Like Ghrelin, Leptin, and Cortisol
-
Ghrelin: Known as the “hunger hormone,” ghrelin stimulates appetite and plays a role in weight regulation. On a keto diet, ghrelin levels are often reduced, leading to decreased hunger and easier calorie control.
-
Leptin: Leptin is responsible for signaling to the brain when you are full. The keto diet may help improve leptin sensitivity, ensuring that your body receives accurate signals of fullness and reducing the chances of overeating.
-
Cortisol: Cortisol is a stress hormone that can impact fat storage and metabolism. While prolonged stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels and hinder weight loss, the keto diet can help regulate cortisol production by stabilizing blood sugar levels and improving overall metabolic health.
The Role of Muscle Mass and Protein Synthesis
A key element of a healthy metabolism is maintaining muscle mass, as muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat tissue. The keto diet supports muscle preservation by providing sufficient protein to maintain muscle tissue while encouraging fat loss.
By maintaining a proper intake of protein, the keto diet supports protein synthesis, which is essential for building and repairing muscle. Muscle mass, in turn, contributes to a higher metabolic rate, as the body expends more energy to maintain muscle tissue compared to fat.
Keto Diet and Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR)
Resting metabolic rate (RMR) is the number of calories your body burns while at rest. It is influenced by factors like age, gender, muscle mass, and hormone levels. Many studies have shown that the keto diet can help increase or maintain RMR, particularly during periods of weight loss.
When you reduce carbohydrates and increase fats, your body burns more fat for energy, which can help maintain or even increase RMR. By preserving lean muscle mass and reducing fat storage, the keto diet ensures that your metabolism remains active and efficient, even while you’re not exercising.
How Keto Supports Metabolic Processes by Improving Insulin Sensitivity
One of the key benefits of the keto diet is its ability to improve insulin sensitivity. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When you consume a lot of carbs, your body releases more insulin, which can lead to insulin resistance over time. However, the keto diet helps regulate insulin levels, preventing insulin resistance and allowing your body to use fat more efficiently.
The Science Behind Fat Burning on Keto
The science behind fat burning on keto is simple: by switching your body’s primary fuel source from glucose to fat, you allow your body to tap into its fat stores for energy. This leads to a continuous cycle of fat burning throughout the day, even while you’re not exercising. Because fat is more energy-dense than carbs, your body burns more calories while in ketosis.
How Ketosis Encourages the Body to Burn Stored Fat for Energy
When you follow a keto diet, your body’s insulin levels drop, and fat cells become more accessible. Instead of storing fat, your body starts to release it for energy. This is what makes the keto diet so effective at promoting fat loss, as it helps your body tap into fat stores rather than accumulating more fat from excess carbs.
How the Body’s Fat-Burning Mechanisms Work While on Keto
Fat-burning mechanisms work more efficiently while on keto because your body is constantly breaking down fat for fuel. The high-fat content in your diet ensures that your body has a constant supply of energy from fat stores, while the low carb intake prevents new fat from being stored.
How the Keto Diet Enhances Insulin Sensitivity
Understanding Insulin Resistance and Its Role in Metabolism
Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This leads to higher insulin levels and can cause weight gain, increased fat storage, and difficulty burning fat. Insulin resistance is often linked to metabolic conditions like type 2 diabetes and obesity.
How the Keto Diet Reduces Insulin Spikes and Improves Insulin Sensitivity
The keto diet reduces insulin spikes by stabilizing blood sugar levels. By cutting out most carbs, your blood sugar remains more stable, reducing the need for insulin production. As a result, insulin sensitivity improves, allowing your body to process glucose more effectively and burn fat more efficiently.
The Long-Term Benefits of Better Insulin Management on Metabolism and Fat Loss
Long-term insulin sensitivity is essential for maintaining a healthy metabolism. By improving insulin sensitivity through the keto diet, your body can more effectively regulate fat storage, control blood sugar, and boost metabolism. This can lead to sustained weight loss and a lower risk of metabolic diseases.
Conclusion
The keto diet is more than just a low-carb diet; it’s a powerful metabolic enhancer. By shifting the body from burning carbs to burning fat, the keto diet helps you achieve a faster metabolism, improved fat-burning capacity, and better overall metabolic health. Whether you’re looking to lose weight or improve your insulin sensitivity, the keto diet provides numerous metabolic benefits that can help you achieve your goals.
Read Also; 7 Powerful Benefits of Keto for Metabolic Health You Shouldn’t Ignore
FAQs https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FAQ#:
How long does it take for the keto diet to improve metabolism?
It typically takes a few days to a week for your body to enter ketosis and begin experiencing the full metabolic benefits of the keto diet. However, results can vary based on individual metabolism.
Can the keto diet be sustainable for long-term metabolic health?
Yes, the keto diet can be sustainable for long-term metabolic health as long as it is properly balanced and followed with adequate nutrients and healthy fats.
Does the keto diet work for everyone when it comes to improving metabolism?
While many people experience improvements in metabolism on the keto diet, individual results can vary. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider or nutritionist to determine if keto is right for you.
Can the keto diet help with other metabolic conditions besides weight loss?
Yes, the keto diet has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce blood sugar levels, and potentially help with conditions like type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
What are the key metabolic benefits of ketosis aside from fat loss?
In addition to fat loss, ketosis can lead to improved energy levels, better blood sugar control, reduced inflammation, and increased mental clarity.




One Comment