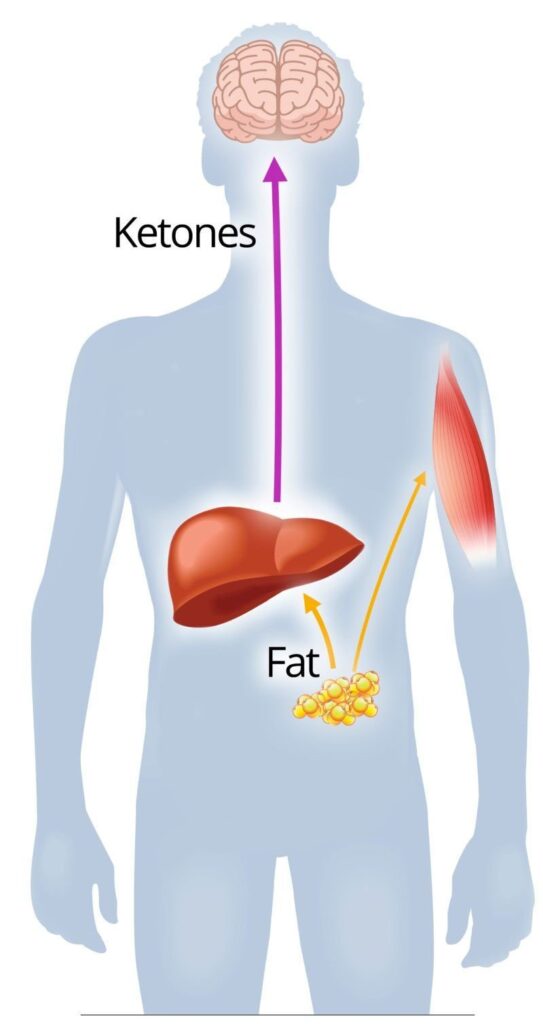
The science behind the keto diet is rooted in the way the body processes nutrients. Unlike other diets that rely on carbohydrates as the primary energy source, the keto diet drastically reduces carb intake and encourages the body to burn fat instead.
- Overview of the keto diet’s rise in popularity
- The science behind the keto diet and why it works
- What to expect from this post
What is the Keto Diet?
- Basic principles of the keto diet
- How it differs from other diets
- The macronutrient breakdown on a keto diet
The Role of Ketosis in the Keto Diet
- What is ketosis and how does it work?
- Benefits of ketosis for weight loss
- How ketosis changes the body’s energy system
The Science Behind Burning Fat on Keto
- Why the body shifts from burning carbs to fats
- Fat adaptation process in the body
- The impact of fat burning on weight loss and metabolism
How the Keto Diet Affects Insulin and Blood Sugar
- The role of insulin in metabolism
- How the keto diet regulates blood sugar levels
- Benefits for people with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
The Impact of the Keto Diet on Brain Function
- How the brain uses ketones for energy
- Cognitive benefits of the keto diet
- The potential for treating neurological disorders
Long-Term Sustainability and Health Benefits of the Keto Diet
- Can the keto diet be followed long-term?
- Potential health benefits beyond weight loss (heart health, cholesterol levels, etc.)
- Common challenges and how to overcome them
Potential Side Effects and How to Mitigate Them
- The “Keto flu” and how to manage it
- Possible digestive issues and nutrient deficiencies
- Long-term health concerns to consider
How to Get Started on the Keto Diet
- Planning meals and macronutrient targets
- Common mistakes to avoid when starting the keto diet
- Helpful tools for tracking your keto journey
Conclusion
- Summary of key points about the keto diet science
- Final thoughts on adopting the keto lifestyle
FAQs
- Is the keto diet safe for everyone?
- How fast will I lose weight on keto?
- Can I eat fruits on the keto diet?
- How can I tell if I’m in ketosis?
- What can I do if I experience the keto flu?
7 Essential Insights into the Keto Diet Science
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as the keto diet, has been gaining popularity over the past few years, thanks to its potential benefits for weight loss, improved energy levels, and better mental clarity. But what exactly is the science behind the keto diet, and how does it work to deliver these impressive results? In this post, we’ll explore the key scientific insights that explain why the keto diet is effective, and how it impacts the body, metabolism, and overall health.
Introduction
The keto diet has evolved from being a niche dietary approach for epilepsy management to one of the most talked-about diets in the world. Celebrities, health influencers, and nutritionists alike have hailed the keto diet for its effectiveness in helping people lose weight and boost energy levels. But despite its popularity, there’s still a lot of confusion about how it actually works and why it’s so effective.
The science behind the keto diet is rooted in the way the body processes nutrients. Unlike other diets that rely on carbohydrates as the primary energy source, the keto diet drastically reduces carb intake and encourages the body to burn fat instead. This process, known as ketosis, has powerful effects on the body’s metabolism, and understanding it can help you make the most out of the keto diet.
In this article, we’ll take you through seven essential insights into the keto diet science, exploring the mechanics of ketosis, the benefits it offers, and how you can optimize the diet for better results.
What is the Keto Diet?
The keto diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate diet that forces the body to burn fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. Typically, on a keto diet, you would aim to consume about 70-80% of your daily calories from fats, 20-25% from protein, and only 5-10% from carbohydrates.
The primary goal of the keto diet is to reach a metabolic state called ketosis, where the body starts breaking down fats into ketones, which are used for energy in place of glucose (the typical energy source from carbs). This shift in energy production helps the body burn fat more efficiently, leading to weight loss.
The keto diet is often used for weight loss purposes, but it has also been studied for its potential therapeutic effects in managing certain health conditions, such as epilepsy, type 2 diabetes, and even neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
The Role of Ketosis in the Keto Diet
What is Ketosis and How Does it Work?
When you eat a typical high-carb diet, your body converts carbohydrates into glucose (sugar), which is then used for energy. However, when you drastically reduce carbohydrate intake, your body runs out of glucose to burn for fuel. In response, the liver begins to convert fats into ketones, which are used by the body for energy. This process is known as ketosis.
In ketosis, your body switches from burning sugar to burning fat, and this is one of the key reasons why the keto diet is so effective for weight loss. By using fat as its primary fuel source, your body burns stored fat, leading to significant fat loss over time.
Benefits of Ketosis for Weight Loss
In ketosis, not only does your body burn fat for energy, but it also suppresses hunger and reduces cravings, making it easier to stick to your diet. The presence of ketones in the bloodstream signals to your body that it’s in a fat-burning mode, which means you can burn stored fat more effectively without the constant hunger pangs associated with other calorie-restricted diets.
The Science Behind Burning Fat on Keto
When most people think about the keto diet, they typically associate it with weight loss, fat burning, and a significant shift in how the body utilizes energy. But the question that often arises is: Why does the keto diet make the body burn fat, and how does it work on a scientific level? This question dives deep into understanding metabolic processes, the physiology of fat burning, and how drastically reducing carbohydrate intake transforms the body’s energy system.
How the Body Switches from Burning Carbs to Fats
The Role of Carbohydrates in Energy Production
Under normal circumstances, when you consume a diet high in carbohydrates, your body breaks down those carbs into glucose (a form of sugar). This glucose then enters the bloodstream, causing blood sugar levels to rise. The pancreas releases insulin in response, which helps shuttle glucose into cells to be used for immediate energy. If there’s more glucose than needed for immediate energy, it’s stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles.
However, glycogen storage is limited, meaning once the body’s glycogen stores are full, any excess glucose is converted into fat and stored in adipose tissue. So, when you consume high amounts of carbs regularly, your body stays in a constant state of storing energy rather than burning it.
What Happens When You Cut Carbs?
On the keto diet, carbs are severely restricted—usually making up only 5-10% of your daily caloric intake. By reducing carb intake to such a low level, the body no longer has a sufficient supply of glucose for fuel. Once glycogen stores are depleted, which can take about 2-3 days on a strict keto diet, the body begins to look for an alternative energy source—fat.
This is where the magic of keto happens. Instead of continuing to burn glucose, the body starts breaking down stored fat (both from food and fat reserves) into molecules called ketones. These ketones are then used as an alternative energy source for your body, including your brain and muscles.
Fat Adaptation: How the Body Becomes Efficient at Burning Fat
What is Fat Adaptation?
Fat adaptation is the process by which the body becomes more efficient at using fat as its primary fuel source. When you start the keto diet and drastically cut carbs, the body initially struggles because it’s used to running on glucose. However, after about 1-2 weeks (depending on the individual), the body adapts and begins to utilize fat more effectively.
During the fat adaptation phase, several things happen:
- Increased mitochondrial function: Mitochondria are the powerhouses of cells, responsible for converting energy into usable forms. As the body adapts to using fat, the mitochondria become more efficient at converting fat into energy.
- Increased enzyme production: The body produces more enzymes necessary to break down fat and convert it into ketones.
- Improved fat oxidation: As fat adaptation occurs, the body becomes better at oxidizing (burning) fat, including both dietary fat and stored body fat.
The result? Once fully fat-adapted, your body becomes a fat-burning machine, effortlessly using fat for fuel even when at rest. This is one reason why the keto diet is so effective for weight loss—it trains the body to become efficient at burning fat rather than storing it.
The Role of Ketones in Fat Burning
What Are Ketones?
Ketones are molecules produced by the liver when the body breaks down fat for energy. There are three primary types of ketones: acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), and acetone. These ketones can be used by muscles and the brain as an alternative fuel source, replacing glucose.
There are several benefits to using ketones for energy:
- Efficient energy source: Ketones provide a steady and consistent energy supply, making them a more efficient source of fuel than glucose. Unlike glucose, which is quickly used up and needs to be replenished frequently, ketones can be stored and released in a sustained manner.
- Brain function: Ketones are a preferred energy source for the brain. Unlike glucose, which can lead to blood sugar fluctuations and crashes, ketones provide the brain with steady fuel, often leading to improved mental clarity and focus.
How Ketones Aid in Fat Burning
When your body enters ketosis, ketones not only replace glucose but also signal to the body that it is in fat-burning mode. The presence of ketones in the bloodstream enhances the breakdown of fat, allowing the body to tap into stored fat reserves. This sustained fat-burning process is one of the primary reasons the keto diet is so effective at reducing body fat.
How the Keto Diet Affects Insulin Levels and Fat Storage
Insulin Resistance and Fat Storage
Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When you consume carbohydrates, insulin is released to help bring glucose into the cells for energy. However, when you consume too many carbs over time, your body becomes insulin resistant, meaning it takes more insulin to move glucose into the cells. This insulin resistance is linked to increased fat storage because high levels of insulin promote fat storage and prevent fat burning.
How the Keto Diet Lowers Insulin Levels
By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake, the keto diet naturally lowers insulin levels. With lower insulin levels, the body is no longer in fat storage mode and instead starts burning fat for energy. This reduction in insulin levels is one of the reasons the keto diet is so effective for people who have insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, or type 2 diabetes.
The Impact of Lower Insulin on Fat Burning
When insulin levels drop, the body’s ability to burn fat improves significantly. This is why people often experience rapid weight loss in the initial phases of the keto diet—the body is no longer storing fat, and instead, it is actively burning fat for fuel. Moreover, lower insulin levels also help prevent further fat accumulation, supporting long-term fat loss.
Why Keto Is So Effective for Weight Loss
Rapid Initial Weight Loss
One of the most common experiences when starting the keto diet is rapid weight loss. While much of this initial weight loss is water weight (as glycogen stores are bound to water), the body begins to burn fat after a few days or weeks. As ketosis kicks in, stored fat is used for energy, leading to significant fat loss.
Sustained Fat Loss
Once the body has fully adapted to burning fat, fat loss becomes more sustained. This is due to the continuous use of fat as fuel, even when you’re not actively exercising. The body taps into both dietary fat and stored body fat, making it easier to lose weight without feeling deprived or hungry.
Reduced Appetite and Cravings
One of the biggest benefits of the keto diet is its ability to reduce appetite and food cravings. Ketones are more satiating than glucose, meaning you feel fuller for longer periods. Additionally, lower insulin levels help stabilize blood sugar, which further reduces hunger and cravings for sugar-laden foods.
How to Support Fat Burning on Keto
Exercise and the Keto Diet
While the keto diet promotes fat burning, exercise can help accelerate the process. Physical activity, especially strength training and aerobic exercises, increases the body’s demand for energy, making it easier to burn fat. When combined with the keto diet, exercise helps the body utilize fat stores more efficiently.
Protein and Muscle Preservation
While the keto diet is high in fat and moderate in protein, it’s important to get enough protein to preserve lean muscle mass. Protein plays a vital role in maintaining muscle while the body burns fat, which is crucial for long-term weight loss and metabolism.
Intermittent Fasting and Keto
Combining intermittent fasting with the keto diet can also enhance fat burning. Fasting periods promote ketosis by depleting glycogen stores and encouraging the body to burn fat. This combined approach has been shown to help accelerate fat loss, especially in stubborn areas.
Why the Body Shifts from Burning Carbs to Fats
On a typical high-carb diet, the body is constantly burning glucose as its primary energy source. However, once you cut down on carbs and enter ketosis, the body has no choice but to rely on fat for fuel. This shift happens because the body’s glycogen stores (carbohydrate stores) become depleted, and the liver begins to break down fat into ketones, which serve as an alternative fuel source for your cells.
Fat Adaptation Process in the Body
At the beginning of the keto diet, your body may feel a bit sluggish as it adapts to burning fat for fuel. This is referred to as fat adaptation, and it can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks. During this time, your body will become more efficient at burning fat and producing ketones, making it easier to sustain ketosis and burn fat for energy.
The Impact of Fat Burning on Weight Loss and Metabolism
Once your body has fully adapted to ketosis, it becomes a fat-burning machine. Not only does this help with weight loss, but it also boosts your metabolism, allowing you to burn more calories even when you’re at rest. Additionally, fat burning leads to a more sustained source of energy, helping you avoid the energy crashes that often come with high-carb diets.
How the Keto Diet Affects Insulin and Blood Sugar
The Role of Insulin in Metabolism
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When you eat carbohydrates, your body converts them into glucose, and insulin helps transport that glucose into your cells for energy. However, high levels of insulin can lead to weight gain, insulin resistance, and other metabolic issues.
How the Keto Diet Regulates Blood Sugar Levels
By significantly reducing carbohydrate intake, the keto diet lowers the amount of glucose in the bloodstream. This, in turn, reduces the amount of insulin your body needs to produce. This regulation of insulin is especially beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance, as it helps lower blood sugar levels and prevent dangerous spikes.
Benefits for People with Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes
The keto diet has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, which helps the body regulate blood sugar levels more effectively. By reducing reliance on insulin, the keto diet can help people with type 2 diabetes manage their condition and, in some cases, even reverse it.
The Impact of the Keto Diet on Brain Function
How the Brain Uses Ketones for Energy
When the body enters ketosis, the brain starts using ketones for energy instead of glucose. Ketones are a more efficient fuel source for the brain, providing better cognitive function and mental clarity. Many people report increased focus and concentration once they adapt to the keto diet.
Cognitive Benefits of the Keto Diet
In addition to helping with weight loss, the keto diet can provide cognitive benefits. Ketones have been shown to improve memory, focus, and mental clarity. Some studies even suggest that the keto diet can help treat neurological conditions like epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease.
The Potential for Treating Neurological Disorders
The keto diet has been used for nearly a century to manage epilepsy, and recent research suggests it could be beneficial for other neurodegenerative diseases as well. Ketones provide the brain with an alternative energy source, which can help protect brain cells and improve overall brain function.
Long-Term Sustainability and Health Benefits of the Keto Diet
Can the Keto Diet Be Followed Long-Term?
The keto diet can be followed long-term, but it requires careful planning and consistency. Many people experience significant weight loss and health improvements in the short term, but to maintain those results, it’s important to stay committed to the principles of the diet.
Potential Health Benefits Beyond Weight Loss
Beyond weight loss, the keto diet has been linked to improved heart health, better blood sugar control, and reduced inflammation. It has also been shown to improve cholesterol levels, reduce the risk of certain cancers, and promote overall longevity.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While the keto diet has many benefits, it can be challenging to stick to in the long term. Common issues include the “keto flu” during the adaptation phase, nutrient deficiencies, and social situations that involve carb-heavy foods. However, with proper planning, these challenges can be overcome, allowing you to enjoy the long-term benefits of keto.
Conclusion
The keto diet has emerged as one of the most effective weight loss and health management strategies in recent years. By understanding the science behind ketosis, fat burning, and the impact on insulin and brain function, you can see why the keto diet works for so many people. However, it’s essential to approach the diet with the right knowledge, careful planning, and realistic expectations. When done correctly, the keto diet can provide not only significant weight loss but also long-term health benefits.
Read Also; 5 Key Facts About the Science of the Keto Diet
FAQs https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FAQ
Is the keto diet safe for everyone?
While the keto diet can be safe for many, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting, especially for individuals with certain medical conditions like kidney disease or liver issues.
How fast will I lose weight on keto?
Weight loss varies from person to person, but many people experience rapid weight loss in the first few weeks due to water weight loss and ketosis. Long-term weight loss can occur steadily as fat is burned for energy.
Can I eat fruit on the keto diet?
Yes, but fruits need to be consumed in moderation. Low-carb fruits like berries, avocados, and lemons are great choices.
How can I tell if I’m in ketosis?
Common signs of ketosis include increased energy, reduced appetite, bad breath (sometimes referred to as “keto breath”), and weight loss. You can also test for ketosis using urine strips or a blood ketone meter.
What can I do if I experience the keto flu?
The keto flu is a common symptom during the early stages of keto. To alleviate symptoms, make sure you’re drinking enough water, replenishing electrolytes (potassium, magnesium, and sodium), and eating enough fats and protein.